- Pre-Paid Instrument Providers (PPI)
- Why Nachiket hates PPI model?
- Why Payment Bank?
- What is payment bank?
- M-Pesa: Why India should get Payment banks?
- Payment Banks: Anti-Arguments
- USSD and Conflict of Interest
- USSD connectivity for Banking
- Mock Questions
Pre-Paid Instrument Providers (PPI)
Airtel money is an example of PPI. So, What do they do?
- You give them money (from your regular bank account)
- They give you a “digital wallet” tied with your mobile.
- You can use it to pay bills, shopping, movie tickets etc.
What are the features/characteristics of such PPI?
- They’re regulated by RBI under Payment and Settlements Act of 2007. (More than 20 such companies allowed to run their PPI scheme.)
- KYC norms apply.
- You don’t earn interest rate on the money saved in it
- You can put maximum Rs.50000 in it.
- You cannot ‘pull out’ money from it. (Meaning you’ve to spend. You cannot ask for refund in cash. except under some special models/schemes.)
- Transaction fee applies. Every time you buy something using your Airtel Money account, they charge ~0.5% as commission.
Other examples of PPI:
- Gift cards issued by banks e.g. prepaid.onlinesbi.com/giftcard.html
- Airtel money, Oxigen Prepaid cards
- Paypoint, Zipcash, flipkart wallet, Paytm, Mobikwik
By the way, unlike currency notes, these prepaid instruments are not fungible. For example, if you have 500 Rs. in your Airtel money account, you cannot get it exchanged for 500 Rs. in Oxigen prepaid card. (even if you manage to do it by some jugaad- there will be ~0.5% commission charge, you never get full convertability from one instrument to another instrument.)
For more on fungibiity, click me
Why Nachiket hates PPI model?
Last year, RBI appointed a Committee for financial services under Nachiket Mor. Committee observed that:
- PPI doesn’t offer interest rate. From financial inclusion point of view, this doesn’t help the poor people and small businessmen save their money.
- PPI is a nested payment model: you give money to PPI, they deposit it in an escrow account in some bank. Everytime you do something using digital wallet, they take out money from that escrow account and pay on your behalf. What’s the problem?
- Problem is nested models= they increase “contagion risk”.
- Contagion risk = bad thing happens @one place, then it also leads to more negative outcomes @other places in the market.
Suppose TRAI/Supreme court cancels Airtel’s license for xyz reason, result?
- Direct problem for people who’ve money in Airtel account.
- indirectly, gives an opportunity for some crook to start a baseless rumor via facebook that airtel has deposited all that PPI money into ICICI/xyz bank and now they’ll also go out of business => then juntaa will rush to demand their money back, share prices fall down and so on…. creating instability in the banking-finance system.
- plus, Issues related to account security, KYC etc.
Therefore, Nachiket recommends:
- RBI should NOT give any more licenses to open PPI.
- Still, If anyone is interested, RBI should ask him to become a Banking business correspondent OR apply for Payment Bank license.
Now comes the main topic:
Why Payment Bank?
Nachiket’s thought process is like this:
- Pre-Paid Instrument Providers (PPI) = suck because they don’t pay interest on your money.
- But their basic model /concept is good= You load cash into your mobile (airtel), use it for buy things, pay utility bills and so on. No need to carry cash, cheque book, credit card or visit ATM booth.
Thus, from financial inclusion point of view, PPI model is good, if they gave interest on your money. So, based on that idea, Nachiket recommends RBI to give license to a new type of banks called “payment banks”. [Under the banking regulation Act.]
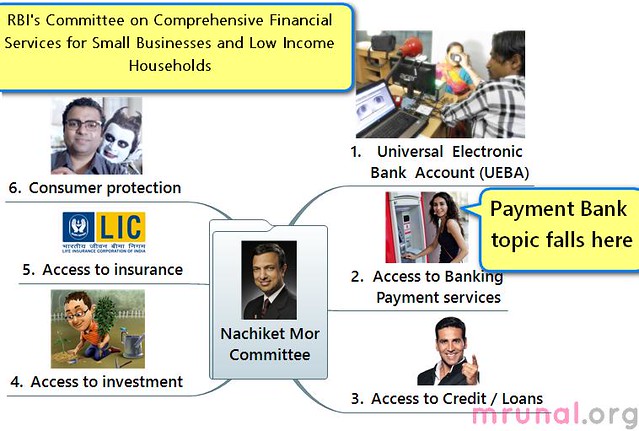
What is payment bank?
Payment banks will have following characteristics:
- Target audience: small businessmen and poor people. (=low income households)
- Potential candidates to run Payment banks: mobile phone companies, consumer goods companies, post office system, agri/dairy type cooperatives and Corporate Business correspondents. Even Scheduled commercial banks can open payment banks as their subsidiaries.
- Payment bank will have to keep CRR (Cash reserve ratio) just like other Scheduled commercial banks (SBI, PNB, BoB, Dena, ICICI etc)
- Payment bank cannot hold more than Rs.50,000 per customer. (This is similar to PPI.)
- Payment bank cannot involve in any credit risk. (again similar to PPI)
more characteristics of Payment banks:
- Payment bank will enjoy all the rights and responsibilities of a Scheduled commercial banks (SCB- like SBI, PNB, BoB, Dena and ICICI)
- Entry capital requirement will be Rs.50 crore.
- Payment bank cannot assume credit risk (meaning they cannot give out loans)
- and since they cannot give out loans=> there is no danger of loan default/NPA.
- Payment bank can invest money in SLR securities, but they are safe investments, you can easily recover money.
- In short, Payment bank faces near-zero risk of default. so, they don’t need a large capital for emergency backup.
side note: Nachiket also recommended wholesale investment banks and wholesale consumer banks. But we’ll see about them in a separate article later. For now, Let’s make a table:
| System | Can Give Loans (Credit)? | Can Accept Retail Deposits? | Can Make Payments? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payments Network Operator (like Mastercard, Visa) | No | No | Yes |
| Payments Bank (Nachiket’s Brainchild) | No | Yes | Yes |
| Sch. Commercial Bank (SBI, ICICI) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| White Label ATM (TATA/Indica$h) | No | No | Yes |
| Bitcoin digital wallet | No | No | Yes (only if both party agree) |
M-Pesa: Why India should get Payment banks?
Nachiket cites the “case study” of M-Pesa, to strengthen his argument in favour of Payment banks. So let’s check what is this M-Pesa?
- M-Pesa is Kenya’s Payment bank. (Fundamentally, it is a Mobile payment service, just like our Airtel Money.)
- M=mobile; Pesa=swahili word for money.
- M-Pesa is the brainchild of Vodafone (=enemy#1 of our Income tax department) + Kenya’s local mobile company called Safaricom +IBM.
- 2006: M-Pesa launched. At this time, more than 70% of Kenya’s Juntaa didnot have bank accounts.
How does M-pesa system Work?
- You go to an M-Pesa outlet (local kiranawalla, shopping center, petrol pump, paan-ki-dukaan etc.)
- Give him cash, he fills up your M-pesa electronic account with that money. (just like how you recharge your prepaid mobile)
- This M-pesa Account is tied up with your mobile phone. Wherever you go, money goes.
- M-pesa helps in money transfer between one person to another, international remittances (e.g. Kenyan worker from USA can send money home), utility bill payments and so on.
- You can even borrow money from Microfinance Institutions (MFI) via mobile phone (and later repay the loans, via same mobile phone).
M-Pesa size and Success:
- Today, More than 75% of Kenya’s juntaa uses M-Pesa system
- More than 25% of Kenya’s GDP flows through M-Pesa system.
- M-Pesa also offers a separate model called “M-Shwari” to give 2-5% interest rate on your money saved in that M-Pesa account.
So, If Payment bank model can succeed in Kenya, it can also succeed in India. (Atleast that’s what Mr.Nachiket believes)
Payment Banks: Anti-Arguments
Bankers have criticized this idea of “Payment banks” because:
#1: Nothing new under the sun
- M-Pesa model you saw above- it is nothing “radically new”- SBI, ICICI and all other big banks already offering such services via mobile banking platform.
- So instead of opening new Payment banks, better just let those existing banks to give these banking-investment-insurance services through their branches, mobile banking, internet-kiosks, business correspondents and bancasurrance model.
- OR Mr.Nachiket could have simply recommended “all PPIs like Airtel money should pay interest on the money held in digital wallets.” instead of coming with a new type of “payment banks”
#2: Not 100% financial inclusion
- Financial inclusion is a bigger thing than mere “payment/money transfer”- Financial inclusion means access to complete bouquet of financial services —banking, investment, insurance, pension – everything.
- But that’s very difficult to achieve through Payment bank system. (Because Nachi himself said, bank cannot assume “Credit risk”.)
#3: Price wars
- Schedule commercial banks also permitted to run Payment banks through their subsidiaries. That defeats the whole purpose because SBI is a giant elephant with large resources and manpower. If it starts a payment bank then other small player’s payment banks cannot compete, and they’ll bleed in price wars.
- in the previous article on White label ATM, we saw how ATM operation costs are hurting the entire banking sector.
- So instead of allowing NBFCs and private companies to open “Payment banks” and compete with regular (commercial) banks, Nachiket should better suggest a model where they all can work in synergy to achieve 100% financial inclusion.
USSD and Conflict of Interest
- Suppose both Airtel and Idea got Payment bank license. I open a payment bank account with Idea but keep airtel phone number.
- Then what if airtel charges more money per SMS when I want to do some net banking /balance inquiry about my Idea BANK account?
- And airtel walla also promises me that if I open Payment bank account in Airtel, they’ll give free services and even discounts @Bharti-walmart malls!
To solve this problem, All mobile companies must be ordered:
- to provide USSD connectivity as per recent TRAI regulations (Rs 1.5 per 5 interactive sessions.)
- to categories all SMSs related to banking and financial transactions as Priority SMS services (with reasonable rates)
USSD connectivity for Banking
USSD=unstructured supplementary service data
- Example of USSD= When you type #123* etc. numbers in your mobile to check balance, activate 2g/3g pack, ringtones etc.
- USSD can be used for prepaid call-back service, location-based content services and menu-based information services.
- Unlike SMSs, USSD messages create a real-time connection during a USSD session.
- The connection remains open, allowing a two-way exchange of a sequence of data making USSD more responsive than services that use SMS.
- Last year, TRAI cameout with guidelines on USSD that:
- For banking related USSD, the mobile company can charge only Rs.1.50 per session.
- This money will be charged on subscribers account (i.e. “balance” in your mobile phone).
- ICICI and SBI have already launched their USSD Based mobile banking services. For example click me for SBI page
Mock Questions
- What do you understand by the term “Pre-Paid Instrument Providers (PPI)”?
- White label ATMs
- Brown Label ATMs
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
- Recently, Nachiket Committee on Financial services, has recommended a new type of Payment banks. Which of the following, is not true about them?
- Scheduled commercial banks will be allowed to open Payment banks as subsidiaries.
- Payment banks will be exempted from CRR and SLR requirement.
- Mobile phone companies, consumer goods companies, post office and cooperative societies will be allowed to apply for Payment bank license.
- None of Above
- Correct statements about Pre-Paid Instrument:
- With RBI’s permission, prepaid instruments are issued in the form of smart cards, internet wallets, or mobile wallets.
- They can be used for purchasing railway tickets, paying utility bills and purchase of goods and services.
- Scheduled Commercial banks can issue such Pre-Paid instruments.
- As per RBI rules, 4% interest rate has to be paid on each such Prepaid instruments
- Find the correct statement(s) about Payment Banks as recommended by Nachiket Mor Committee
- Payment banks will be kept outside the purview of Banking regulation Act.
- Payment banks will be focusing mainly on Service class employees and HNI (High networth individuals).
- Payment banks will have to follow the targets under PSL (Priority sector lending).
- None of above
- Correct Statements about USSD
- USSD facilitates real-time two-way exchange of data between mobile phone and the service provider.
- As per TRAI regulation, mobile companies are requireed to provide all USSD services free of cost.
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
Descriptive/Mains
- Nachiket Committee’s proposed payment banks are better suited to achieve the goal of financial inclusion compared to the existing setup in banking sector. Do you Agree? Justify your stand. (10m | 200 words)
- Write a note on Nachiket Mor Committee’s recommendations regarding Payment Banks. (5m | 100 words)
- Compare and contrast between the proposed Payment banks and Scheduled Commercial banks. (5m | 100 words)
- Define USSD. Explain its utility in Mobile Banking and Financial inclusion. (5m | 100 words)
Visit Mrunal.org/Economy For more on Economy, Banking, Finance, taxation and more.

![[Sci-Tech] rMQR Code (Rectangular Micro QR Code): new invention by the Japanese](https://mrunal.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/rmqr-500x383.png)

payments banks can’t accept time deposits. it means no FD. only demand deposits (SAVINGS ACCOUNT) permitted. please clarify!!