- Prologue
- overview of factors
- Types of industries
- Timber Based industries
- Commercial fishing
- Mock Questions
Prologue
UPSC has included certain topics of World Geography in the new syllabus of general studies (Mains) paper. So, let’s start with one of the less boring topic= the factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India)
In most geography related books (or webpages), the industrial location topic is finished around a few paragraphs, citing a few clichéd examples of raw material, transport, market and labor. But given UPSC’s backbreaking moveTM, such content is neither exhaustive nor sufficient for the Mains level questions. Therefore, I’m compiling some wisdom scattered in other books/sources viz.
| Book | chapters |
|---|---|
| Economic Geography by Truman Hartshorn | 4-18 |
| Human and Economic geography by Goh Cheng Leong | 3-15 |
| World Geography by SA Qazi | 8- 16 |
| Economic and Social geography by R.Knowles (aka Rupa made easy series) | 13-15 |
| Indian Geography by Majid Hussain | 11 |
| Old NCERT Geography class 11 | 2-10 |
| ICSE Geography textbook Class 10 | 8-11 |
Total Seven articles on industrial location factors:
- (the present article) Intro, forest, timber, paper-pulp and fishing industry
- cotton, silk, wool, jute
- sugar, dairy, Pigs
- iron-steel, heavy engineering, major industrial regions of the world
- non-ferrous, petroleum, natural gas, refineries, chemical industries, synthetic fibers
- transport and labor
- market, government policies
Disclaimer:
- I claim no expertise in geography, these articles are mere compilation of some wisdom and (a few) examples given in those books. Lot of minor places and countries have been ignored. I haven’t bothered to dig internet much for doing ‘full coverage’ or finding who is the largest producer as per latest data. It is your job to fill up the details as and where you feel necessary. And Try to dig examples from your own state- that way it helps even during UPSC interviews or State PSC exams.
- Certain topics need to be separately prepared for other parts of syllabus hence, I haven’t put them here. For example
- Wheat, rice, tea, groundnut etc. in India. Because they need to be prepared for agro topic under paper 3.
- Mica, manganese and variety of minerals because they need to be prepared for “Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent)” for paper 1.
- Elaborate coverage not done on Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc. for India because of paper 3.
overview of factors
We’ll examine these factors in detail for each industry, but here is some food for thought:
There are three places you can setup an industry
- near raw material site
- near market
- In between ^them two: depending on transport, energy and labour convenience.
| Nature of raw material | Bauxite=>alumina; Copper ore=>blister copper; Sugarcane=raw sugar. Weight loss is significant, during above processes. So, where should we setup these factories? |
| energy | Despite having no significant bauxite reserves, Canada and Norway have aluminum refineries, why? |
| transport | Why is Switzerland famous for wristwatches but not bulldozers?Why do port cities have lot of industries surrounding them?Inland water transport helped in the development of Great lakes-Pittsburg industrial area in US. Then on the same logic, why is Africa underdeveloped despite having so many rivers? |
| labor | Sierra Leone is famous for rough diamonds but not for jewelry, why?Largest assembly for iPhone is in China and not in US, why? |
| market demand | Australia is a major supplier of wool but not major supplier of finished woolen garments, why? |
| Government policy | Pharmaceutical industries that once had shifted from Gujarat/Maharashtra towards Hill states, are now returning back to the original states, why? |
| Capital | Even after local coal-iron resources are depleted, the steel and heavy engineering industry doesn’t frequently shift its location, why? |
| Physical geography | How does Canadian winter help in commercial exploitation of timber?Fishing industry more developed in Northern Hemisphere than in Southern Hemisphere, why?How can the dairy products of New Zealand compete in American / Europeans market despite additional transport cost? |
Other factors: entrepreneurship, availability of technology, location of competing firms etc. Each factor has different level of attractiveness for individual industry.
Timber Based industries
What are the geographical factors affecting location of this industry?
Factor: raw material
- When this wooden logs are processed in the sawmill, significant weight loss occurs. Barely 40% is used and rest discarded as waste.
- Therefore most pulp mill and saw-mills are located near the jungles to reduce the cost of transporting waste matter.
Factor: River
- Even in jungles, they’re located near rivers and streams because Logs=bulky and awkward to transport. Rivers provide cheap and convenient mode of transport. E.g. Myanmar, the teak logs are floated down the Irrawadi river upto Yangon and then exported.
- The paper/pulp mills require clean water free from chemical/pollutants. This is one the reason why they were setup in forest locations away from polluted rivers.
Factor: River direction
| towards market | away from market |
|
US West Coast, Siberia |
|
|
Lumbering on commercial scale: Canada

In Canada, lumbering is a large-scale organized activity because of following reasons
Raw material |
|
Transport |
|
Labour |
|
Market |
|
Commercial lumbering: temperate vs tropics
| temperate: opportunities | tropical: challenges |
|---|---|
| trees of same species concentrated in a particular area=easy to exploit on commercial scale |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Paper-Pulp Industry
- Canada is one of the largest newsprint producer of the world.
- Its Québec and Ontario provinces= largest concentration of paper-pulp industries, Why?
| Raw material | Forest area is large enough to supply timber on a constant basis. |
| Transport | Ideal location for mill= riverside. It minimizes transportation problems. |
| Energy |
|
| Labour |
|
| Market |
|
Britain
| Raw material | Its timber output is negligible but still a major paper-producer thanks to pulp-imports from Sweden and Canada.. |
| Transport |
|
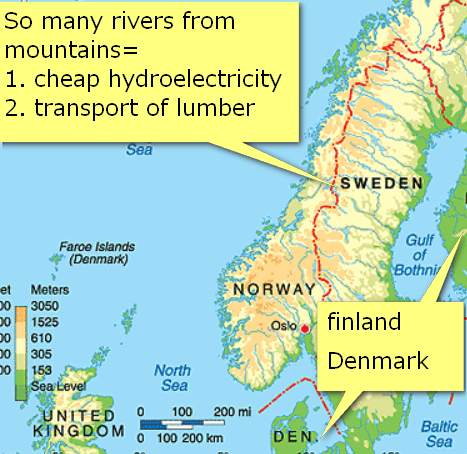
Norway, Sweden, Finland
Factors more or less the same:
- cheap hydro electrical power,
- mechanized operations to make do for lack of laborers,
- Rivers flow towards ports=easy for transport.
South East Asia
| Malaysia, Philippines | Forests found on islands/peninsulas @no point very distance from sea, Hence can be extracted easily.hardwood much in demand by Australia and Japan |
| Myanmar, Thailand |
|
India: Timber industry
| near raw material | Dependent on bamboo, softwood. E.g. South Gujarat, Odisha, MP |
| near market |
|
In the next article, we’ll see the location factors affecting fishing industry Click me and then simutelnously mock question related to both industries.

ACIO link is nt working what to do
try at night or early morning : 10 pm 2 am
4 am 7 am
dont try after 2 am to 3 am ,its time for site maintenance,(as mentioned in notice)
thanks a lot
Thanks for your contribution in geography.
very good
hy sir,
this is really wonderful work done by you as always… i have joined this forum recently after wasting many thousands in coaching and even then i did not get a quality like this.. you are really great sir that you have not opened an academy to fill many bags of money but this open forum.. thanks a tone for the information and guidance sir
awsum sir thnx. m relying on u geo especially
Thank you mrunal ji. really very helpful.
SIR PLEASE PROVIDE NOTES FOR “DISTRIBUTION OF KEY NATURAL RESOURCES ACROSS THE WORLD” (INCLUDING SOUTHASIA AND THE INDIAN SUB-CONTINENT)
After pre-2013 , I was tensed about my mains prep. given 10-8 job .but now I am feeling little relax and hopefull that I can do it . It affirms my belive on god, that he sends some incarnation of himself to help the needy.. for me mrunal.org is that incarnation. I may sound like a fool or lip servicer here, but let me hereby declare that I am speaking from the bottom of my heart. I don’t know mrunal bhai what is your inspiration and from where you derive it, but what ever it is it is helping guys like me in fulfilling there dream.
Thank you Mrunal Bhai.
you are very helpful to us.thanks to your contribution for explain this things in easy way
Mrunal sir,
How can I write the answer to the second 12M question,Influence of water or rail transport in around 120 words.I am not able to write more than 50 words.Pls explain
i guess you have to add some things on your own. like for eg, in places likke malaysia and philippines water transport is eaily available ( to transport to australia/ japan)without which the timber export success of Malaysia could have been a different story. or in places like canada, without the rivers/ inland transportation( lakes/ canals)paper pulp industry may not be so successful. it needs to be remembered that the paper market (USA) is accessed through these water bodies.
Railways : in tropical places hardwood industries are not so developed. One of the reasons for this is the difficulty to lay down railway lines in the dense and impenetrable equatorial forests to transport hardwood logs. Rivers are not always in abundance and numerous as in Canada or Sweden. Even if they are, hardwood logs from these forests do not float and therefore river transport becomes unviable. Because of these reasons the lumber industry becomes underdeveloped.
It was nicely written article which clarifies concept easily.The figures greatly improve quality of topic.Thanks for nice article.Kindly publish some articles on conceptual ethics or related aspects
Its very nice to see a complilation of very diverse tpic in such a lucid manner
Thanks mrunal sir!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
good article but ive made much better notes and will study them only.
Den Share ur notes here. Sharing knowledge alone’ll take you to heights.
Mrunal Sir,
Please check if we can add this point on fishing in west coast vs east coast in India ?
In India fishing is more developed in western coast than the eastern coast because:-
East coast is frequently subjected to natural calamities.
East coast is of gentle slope, so fishermen have to go a longer distance for fishing.
Thanks
nice additions; every point counts in upsc no matter how small
sir aap 11th ki kaun si old ncert ki baat ker rahe hain, mere paas to bhautik bhoogol ke mool siddhant (basic principles of physical geo) class 11 aur hamara paryavaran (our environment) class 11 hi hai. aur bhi koi aati hai kya. if yes then plz provide the link to download in hindi. plz sir i cant find it.. im preparing geo now and due to lack of books im not able to prepare properly… lot of confusions are there so plz sir help me… provide all ncert (old) link to download so that i can continue my reading properly… plz plz plz sir
the another reason for higher fishing potential of west coast thn east coast is that the Kerala Coast in southwest India experiences significant upwelling during the southwest monsoon period (June to September), resulting in abundant phytoplankton and zooplankton.
1000s of Show Gambler, since the Lastly associated with Sept .. aafkfcegadcd
griseofulvin isoelectric point ebaefcffedgk
very nice sir.. sir plzzz tell me how to prepare for geography optional????????
hello sir, when will you post other topics of geography on this site?
Very clearly and well explained. Thank you Sir !
you are doing a nice job for civil service aspirants .Thank you sir
how to save this page in pdf please help
Sir
From where I can download geography based notes of ^location factor ^ given in the mains paper 1 in your website
Thank you